Edgar Mitchell standing by the deployed U.S. flag on the lunar floor throughout the early moments of the mission’s first spacewalk.
| Photo Credit: Photo: HO / NASA / AFP
When we discuss the Apollo programme, it’s typically arduous to look past the Apollo 11 mission, which achieved the distinction of landing the first people on the moon. Even although the Apollo programme is greatest remembered for this, it must also be famous that it supplied for innumerable demonstrations of ingenuity and drawback fixing and elevated NASA’s experience by leaps and bounds.
Following the success of Apollo 11 in July 1969, Apollo 12 landed people on the moon in November 1969. Apollo 13, nevertheless, needed to be aborted following an oxygen tank explosion in the service module. This meant that the Fra Mauro Formation, initially deliberate to be the lunar landing web site for Apollo 13, served as the landing web site for Apollo 14, as soon as NASA had accomplished an accident investigation and upgraded the spacecraft.
Shepard, Mitchell and Roosa

Apollo 14 astronauts (left to proper) Stuart Roosa, Alan Shepard and Edgar Mitchell forward of their January 31 blastoff to the moon.
| Photo Credit:
PHOTO: THE HINDU ARCHIVES
Launched on January 31, 1971, Apollo 14 had a three-member crew that included commander Alan Shepard, lunar module pilot Edgar Mitchell, and command module pilot Stuart Rossa. Even although there was a possible quick circuit in an abort change on the lunar module and the landing radar got here on very late throughout the landing sequence, Shepard and Mitchell efficiently landed on the lunar floor on February 5. In truth, it was the most exact landing till then, as they landed lower than 100 toes from the focused level.
Shepard and Mitchell spent over 33 hours on the moon, together with two additional vehicular actions (EVAs) that spanned 9 hours and 23 minutes. Even although the first of the two EVAs started an hour later than scheduled as a consequence of communications programs issues, it turned out to be successful.
The first EVA was primarily to deploy quite a lot of experiments and a few of these despatched again information to Earth till September 1977. While a seismometer detected 1000’s of moonquakes and helped discover out the moon’s inner construction, different devices checked out the composition of photo voltaic wind and the moon’s ambiance.
Modular Equipment Transporter
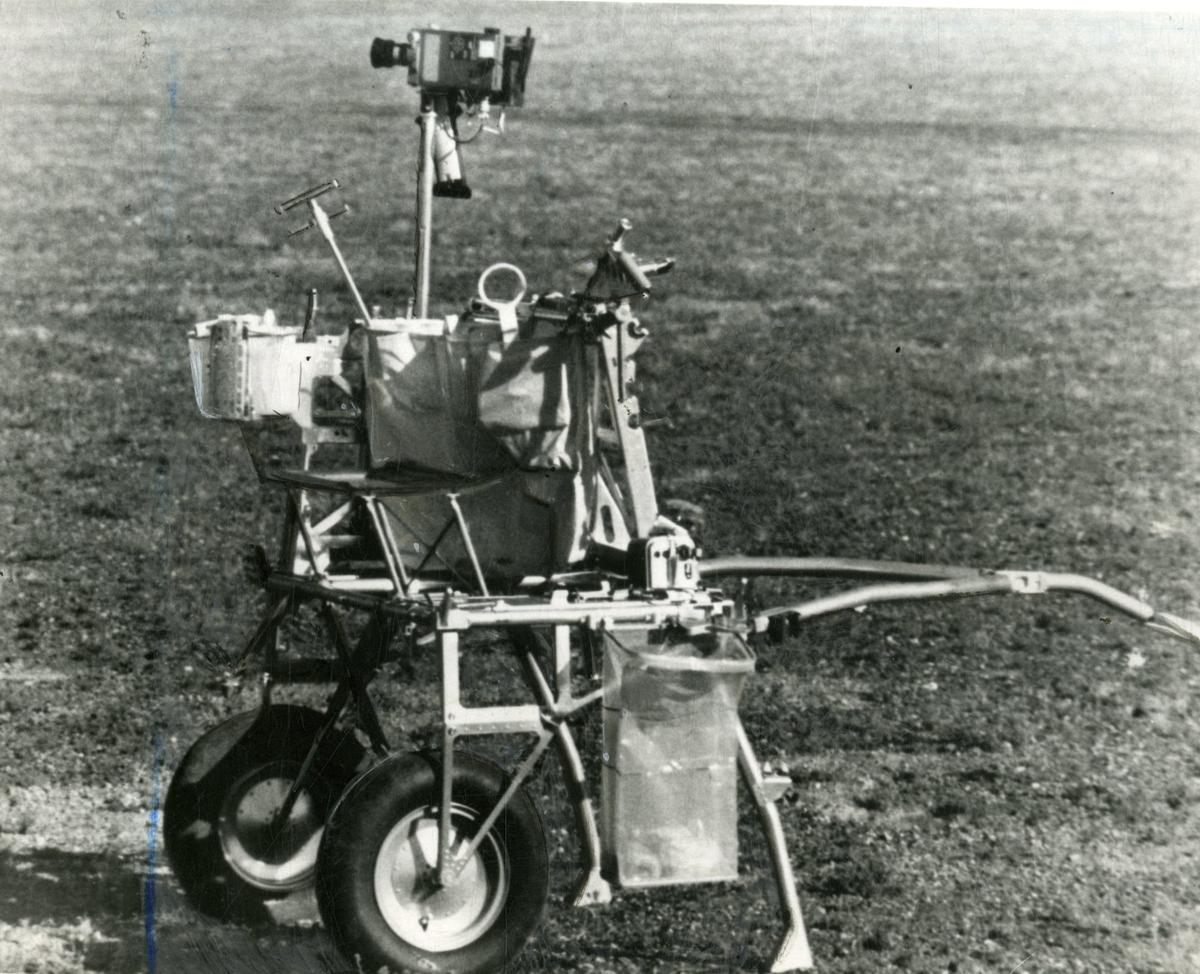
An in depth-up view of the modular tools tranporter (MET).
| Photo Credit:
PHOTO: THE HINDU ARCHIVES
Apart from the security upgrades that had been completed for Apollo 14, there was additionally the addition of the Modular Equipment Transporter (MET). While Apollo 11 astronauts carried their instruments by hand and Apollo 12 astronauts used a hand device provider, Shepard and Mitchell may make use of the MET like a wheelbarrow, stowing away their scientific tools, instruments, digicam, and pattern collections.
During the duo’s second EVA devoted to discover the Cone Crater, the MET got here in helpful as they had been in a position to decide up a football-sized rock, designated 14321, however higher identified by its nickname “Big Bertha.” Using the MET, the astronauts had been in a position to transport this pattern again to the lunar module. As lately as 2019, research instructed {that a} 2 cm sliver of the Big Bertha might need initially come from the Earth’s crust, and never the moon.
42 kg of samples
Even although the crew by no means noticed the inside of the crater, post-mission comparisons confirmed that Shepard and Mitchell had been inside 50-75 m from the crater rim. The spherical journey lasted 4 hours and 35 minutes through which the duo traversed almost 3 km. Including samples from the first EVA, the duo had collected 42 kg of lunar samples.
While Shepard and Mitchell had been busy on the lunar floor, Roosa, who was in the command module, clicked many footage in excessive decision. These pictures of the moon’s Descartes area performed a pivotal position in certifying the space’s security as a landing web site and even helped plan rover traverses for the Apollo 16 mission.
Liftoff from the lunar floor came about precisely on schedule, whereas rendezvous and docking with the command module was simply two minutes off schedule. After spending 2.8 days in lunar orbit, throughout which era the command module had circled the moon 34 occasions, the Apollo 14 crew members headed again to Earth. They splashed down safely in the Pacific Ocean on February 9, precisely 9 days and two minutes after launch.


