The story up to now: Dengue is the world’s fastest-growing vector borne illness: proof reveals over the previous 50 years, there was a 30-50-fold enhance in dengue instances in tropical and subtropical international locations, like India. While dengue is largely accepted as an annual epidemic in a number of international locations (impacting greater than 3.6 billion individuals) recurring each monsoon, the face and anatomy of the illness are altering.
A new research led by researchers on the Indian Institute of Science discovered the dengue virus has developed “dramatically” during the last 5 many years in India. A Lancet research this yr drew a comparable conclusion, including that urbanisation, inhabitants development, rising temperatures, and local weather change created “conditions for the dengue vectors and viruses to multiply”. In April, Argentina noticed its worst dengue outbreak in 25 years.
There is no particular drugs or treatment for dengue, making vaccines essential in stopping an infection and illness development. However, growing a common vaccine has remained a problem.
The science of dengue vaccines
Dengue is transmitted to people by the Aedes mosquito species, A e. aegypti or Ae. albopictus, which additionally spreads Chikungunya and Zika virus. There are 4 serotypes (or sorts) of the dengue virus — DEN-1, DEN-2, DEN-3 and DEN-4 — every virus interacting in a different way with antibodies within the human physique. Each serotype is able to manifesting into dengue fever, dengue hemorrhagic fever and dengue shock syndrome.
The manifestation of dengue virus an infection. Photo Credit: WHO
Five sorts of dengue vaccines are presently being investigated: reside attenuated vaccine (which makes use of the weakened or “attenuated” type of the virus, such because the measles or chickenpox vaccine); inactivated vaccine (utilizing the lifeless virus, used for Hepatitis A and rabies), recombinant subunit vaccine (as in COVISHIELD, the place non-structural proteins of the dengue virus are used, aiding a balanced immune response), viral vectored vaccine (such because the vaccine towards Ebola) and DNA vaccine (for HIV, malaria, TB).
Progress of vaccine trials
The first documented (albeit unsuccessful) medical trial dates again to 1929, when scientists used virus inactivated utilizing phenol or bile; then throughout World War II, scientists used weakened strains of DEN-1 and handed it by way of mouse mind.
Sanofi Pasteur’s Dengvaxia, a reside attenuated vaccine, was the primary vaccine to obtain a nod in 2015, and has been licensed in 20 international locations (not in India) since. Other key gamers embody Takeda’s Qdenga (TAK-003), which was just lately authorized in Brazil and Indonesia, and by the U.S. Food and Drugs Administration (FDA) for precedence clearance in November 2022. Another live-attenuated vaccine (TV003/TV005) was developed by the U.S. National Institutes of Health. The TV003/TV005 was licensed to 3 well-established producers in India (and in China, Japan and Europe) and is below medical trials.
A number of different vaccine candidates are in various pre-clinical and medical trial levels. The Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR) in November final yr sought approval for medical trials of a vaccine in works with drugmakers Serum Institute of India and Panacea Biotec. Per a latest Hindu report, Panacea’s vaccine is conducting Phase-III randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial in 10,335 wholesome adults (aged 18-80 years) in 20 websites (ICMR-funded), and the trials had been authorized by the Drugs Controller General of India in January this yr. Serum Institute of India’s vaccine has initiated one-two research within the paediatric inhabitants.
Also below analysis are 19 DNA dengue vaccines, that are yet to achieve ultimate medical trials, as of 2021.
The image of a perfect vaccine is thus: it needs to be protected, supplies full long-lasting safety towards all 4 serotypes (in order to keep away from sickness after recurring an infection), reasonably priced and accessible at an preliminary stage, and is in a position to weaken the virus while making the physique immune (immunogenicity) to subsequent infections.
Why is there no vaccine yet?
Experts ascribe the lag to a dearth of analysis round totally different dengue sorts; the evolving ‘inimitable’ nature of the virus, making vaccine growth a dynamic problem; apprehensions over vaccine security; lack of funding for a illness that predominantly impacts poorer populations.
An individual may be contaminated with DEN-1, recuperate with antibodies, however get reinfected with DEN-3 later. The 4 serotypes successfully require analysis for 4 totally different vaccines — as a result of one could also be protected towards one serotype for all times, however not towards the opposite sorts. It is troublesome to develop a vaccine that successfully targets all 4 serotypes, consultants say. Takeda’s vaccine claims to guard towards all 4 sorts, however there’s a want to watch long-term information, consultants say.
Another problem pertains to testing: the dearth of a low-cost, accessible and delicate animal mannequin which mimics immune responses in people after an an infection. Mice, as an example, are immune to dengue an infection in itself. The consensus amongst consultants is laboratory animals, used for testing dengue vaccine efficacy, do not mirror the illness’s development in people precisely.
The India story
India contributes a third of the overall international dengue burden
Dengue has witnessed greater than a fivefold enhance from 28,066 instances in 2010 to 157,315 instances in 2019 in India, as per information from the National Vector Borne Disease Control Programme
Dengue deaths show to be dearer than extreme hospitalised non-fatal dengue instances, as much as 90% of those prices had been out-of-pocket expenditures, as per a paper which checked out instances between 2017-18 in Vellore ( International Journal of Infectious Diseases, Vol. 84, July 2019)
India’s main vector management interventions for dengue embody controlling the mosquito inhabitants, spraying larvicide in containers that the dengue carrying mosquitoes breed in, indoor area spraying and out of doors fogging
The virus is evolving too, and the way the human physique responds to it is turning into advanced. Dr. Neelika Malavige, a Sri Lanka-based researcher and physician who has studied dengue’s unfold, notes many international locations are experiencing a shift within the inhabitants pyramids; earlier dengue instances had been extra prevalent amongst youngsters, now instances are rising amongst younger adults. As the Indian Institute of Science research additionally discovered, DEN-1 and DEN-3 had been the dominant strains in India till 2012, submit which DEN-2 accounted for almost all of instances. In latest years, instances of DEN-4, which was as soon as thought of the least infectious, is now generally being reported in elements of South India.
The researchers checked out genetic information of serotypes between 1956 and 2018 to search out a deviation: the genetic sequence strayed from ancestral patterns and did not match international patterns. This might be because of Antibody-Dependent Enhancement (ADE), when somebody contaminated with one serotype develops a second an infection with a totally different serotype, resulting in extra extreme signs. ADE could not solely improve the severity of the an infection, the analysis discovered, but additionally change the traits of the virus itself. Vaccines work by triggering the immune system, which produces antibodies to struggle the an infection. Dengue antibodies do the alternative — the virus makes use of the antibodies itself, giving a increase to the virus, making a second an infection extra harmful.
Studying populations with earlier infections presents a region-specific analysis hole that can have a bearing on how efficient a vaccine is for a specific goal group. Rahul Roy, one of many authors of the research, mentioned that whereas evaluating the range of Indian variants, “we found that they are very different from the original strains used to develop the vaccines”. In different phrases, analysis for present vaccines could not account for the virus’s traits in international locations by which dengue is most endemic. “Such insights are possible only from studying the disease in countries like India with genomic surveillance because the infection rates here have been historically high and a huge population carries antibodies from a previous infection,” mentioned Mr. Roy.
Also learn | Climate change growing threat of latest rising viruses, infectious illnesses in India
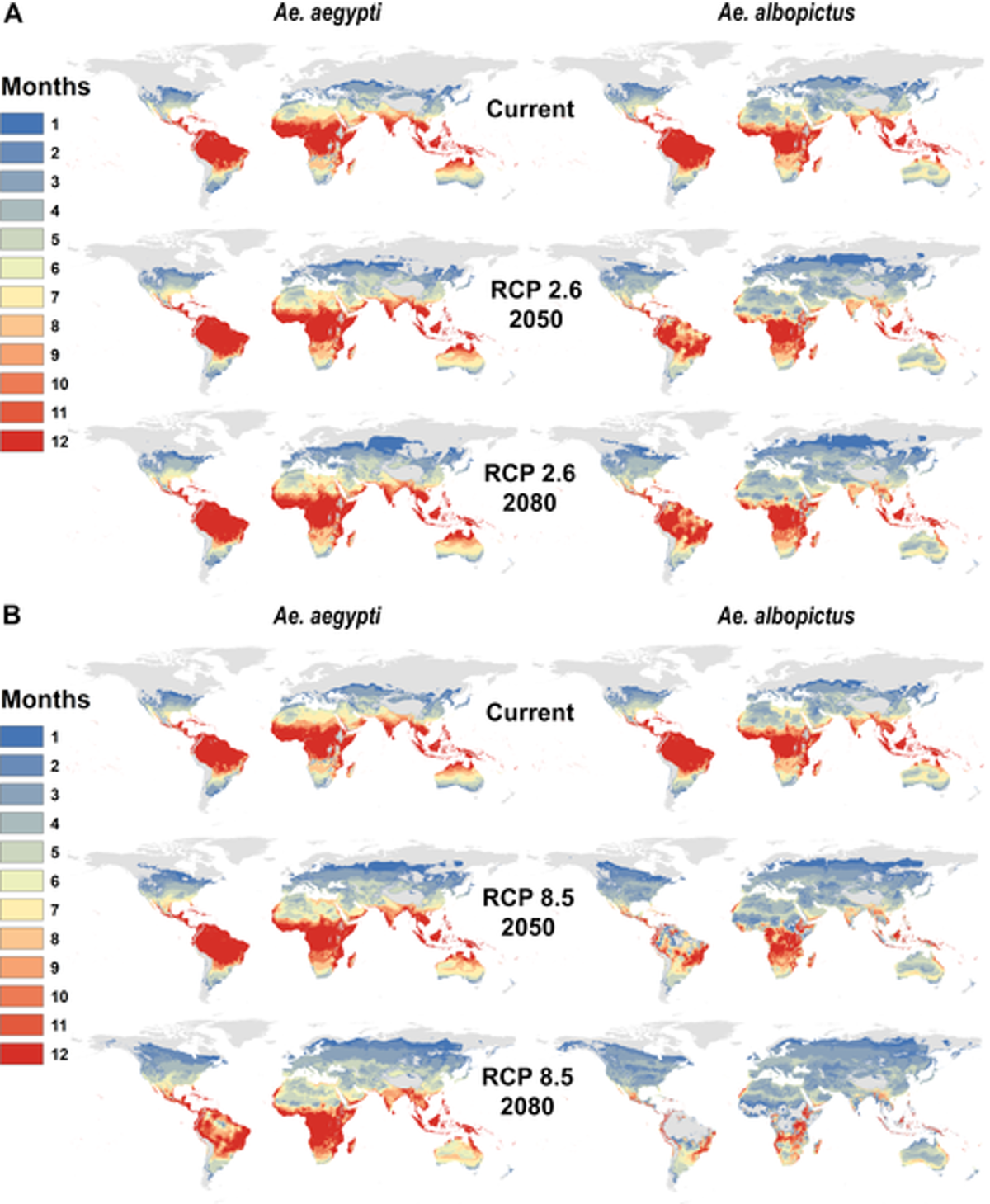
The illness is turning into harmful, not solely because of human vulnerability but additionally local weather change and urbanisation. Climatic components — together with temperature, humidity and rainfall — influence the life cycle and transmission of vector-borne viruses (equivalent to dengue and malaria), such that they can develop sooner, survive for longer durations of time within the host inhabitants and unfold to geographies with out histories of reported an infection. Transmission months of the virus have elevated too, analysis reveals, because of shifting monsoon and urbanisation. The variety of months appropriate for dengue transmission by Aedes aegypti mosquitoes has risen to five.6 months annually, per a 2022 Lancet report
Prior to 2010, Bihar recorded virtually zero instances of dengue, excluding any main outbreaks. The caseload reached 6,712 infections in 2019. “The spread of dengue fever in rural and semi-urban areas is a matter of concern for public health and it can be correlated with unusual climatic patterns arising on account of global warming,” a 2019 research confirmed. A more moderen research projected “expansion of Aedes aegypti in the hot arid regions of the Thar Desert and Aedes albopictus in cold upper Himalayas as a result of future climatic changes”.
Global growth and redistribution of Aedes-borne virus transmission threat with local weather change. Photo Credit: Ryan SJ, Carlson CJ, Mordecai EA, Johnson LR (2019)
Previously reported adversarial occasions to the vaccine could have solid a pall on future growth, some say. Take Dengvaxia, the world’s first licensed dengue, which WHO beneficial for kids aged 9 to 16 years. Almost 14 youngsters in Phillippines who acquired the vaccine died, and a number of other others had been hospitalised. It was discovered that the immune responses to some dengue virus serotypes waned with time, particularly in those that had been not contaminated with any dengue virus beforehand. In its evaluation, WHO famous the vaccine “may be ineffective or may theoretically even increase the future risk of [being] hospitalised or severe dengue illness”. Dengvaxia’s efficacy is restricted to these with confirmed earlier infections (individuals dwelling in endemic areas), however its use has declined as a result of it’s troublesome to check people if they’ve had dengue up to now, says Dr. Malavige.
Research is thus wanted to know how the genetics of various kinds of dengue differ, their distribution and the way the virus evolves.
Dengue is massively prevalent. Why is there not sufficient funding for R&D?
Dengue is a uncared for tropical illness, one in every of 20 recognised by the World Health Organisation. These illnesses are traditionally concentrated amongst low-income international locations, turn into a “proxy for poverty and disadvantage”, as WHO notes, and thus are ‘non-profitable markets’. Joelle Tanguy, Director of External Affairs on the Drugs for Neglected Diseases initiative (DNDi), in a weblog submit, famous, “There is a pressing need to prioritise R&D for climate-sensitive diseases for which drugs and diagnostics are not developed or are not available, as the medical and pharmaceutical industry focuses on more profitable markets.”
Dengue is additionally encased in a data hole. There is little or no public training, say, about how dengue an infection impacts pregnant girls or could affect outcomes throughout childbirth, or how dengue worsens with local weather change. It is relegated as a non-urgent, recurring endemic that doesn’t demand as a lot power or funding as a international pandemic ought to.
“The fact is that very little funding is available for dengue and to answer these very important questions.”Dr. Neelika Malavige
The funding is linked to lack of information, and a sense of misinformed complacency. Radha Pradhan, who works as a nurse coach with Antara Foundation in Madhya Pradesh and comes throughout such instances, mentions a vital data hole amongst native healthcare staff as nicely. For individuals working in areas the place dengue instances have traditionally been low however are actually rising, it turns into a concern as a result of “those who haven’t experienced cases, they won’t be able to tell the basic symptoms and differences about dengue diagnosis.”
The unfavourable historical past of security dangers may current a problem to how the vaccine is accepted, extra so by weak teams equivalent to youngsters and pregnant girls. For vaccine acceptance of any variety, nonetheless, consciousness and data of dengue’s anatomy is crucial, consultants say.
What does dengue remedy appear to be proper now?
There is no prescribed remedy plan for the dengue virus. The focus stays on treating signs, equivalent to fever and fatigue, and platelet transfusion for these in whom the rely drops drastically. Health practitioners argue for higher diagnostic amenities and public well being infrastructure, for early detection and well timed intervention.
An editorial within the International Journal of Infection Diseases acknowledges that the event and testing of dengue vaccines, together with a concerted nationwide effort to ascertain surveillance programs and efficient vector management, may result in a “paradigm shift in global dengue control”.

