Utter devastation: The seek for surivors in a collapsed constructing after the earthquake in Kahramanmaras, Turkey on February 11, 2023.
| Photo Credit: Reuters
The story so far: Two massive earthquakes, one in all magnitude 7.8 and carefully adopted by a magnitude 7.5, hit south-eastern Turkey, claiming not less than 17,000 lives and counting, wreaking appreciable harm in Turkey in addition to Syria. Nearly 200 aftershocks have adopted with earthquakes of magnitude 6 being reported in the area three days after the first tremblor.
What causes earthquakes?
The earth’s crust is made up of roughly 15 large segmented chunky slabs known as tectonic plates that are continually in movement. The land on which buildings are constructed rests on these plates. The plates frequently collide, push and grate towards one another and the assembly factors of those plates are made up of a collection of ‘faults.’
The pent-up vitality from the nestling plates, alongside faultlines, is usually launched when an imbalance in strain causes rocks on both aspect of the fault to re-adjust. One set of rocks rising up relative to the different is a ‘normal’ fault, and one sliding down relative to the different is a ‘reverse’ fault. When they grate or transfer previous each other, it’s a ‘strike-slip.’ The vitality launched travels as waves that trigger the floor to shake.
What type of earthquake occurred in Turkey and Syria?
Turkey and Syria lie at the confluence of three plates — the Arabian Plate, the Anatolian Plate and the Eurasian Plate, making the area an especially seismically lively zone. The Arabian Plate is inching north into Europe, inflicting the Anatolian Plate (which Turkey sits on) to be pushed out west. The bulk of Turkey sits on the Anatolian Plate between two main faults: the North Anatolian Fault and the East Anatolian Fault.
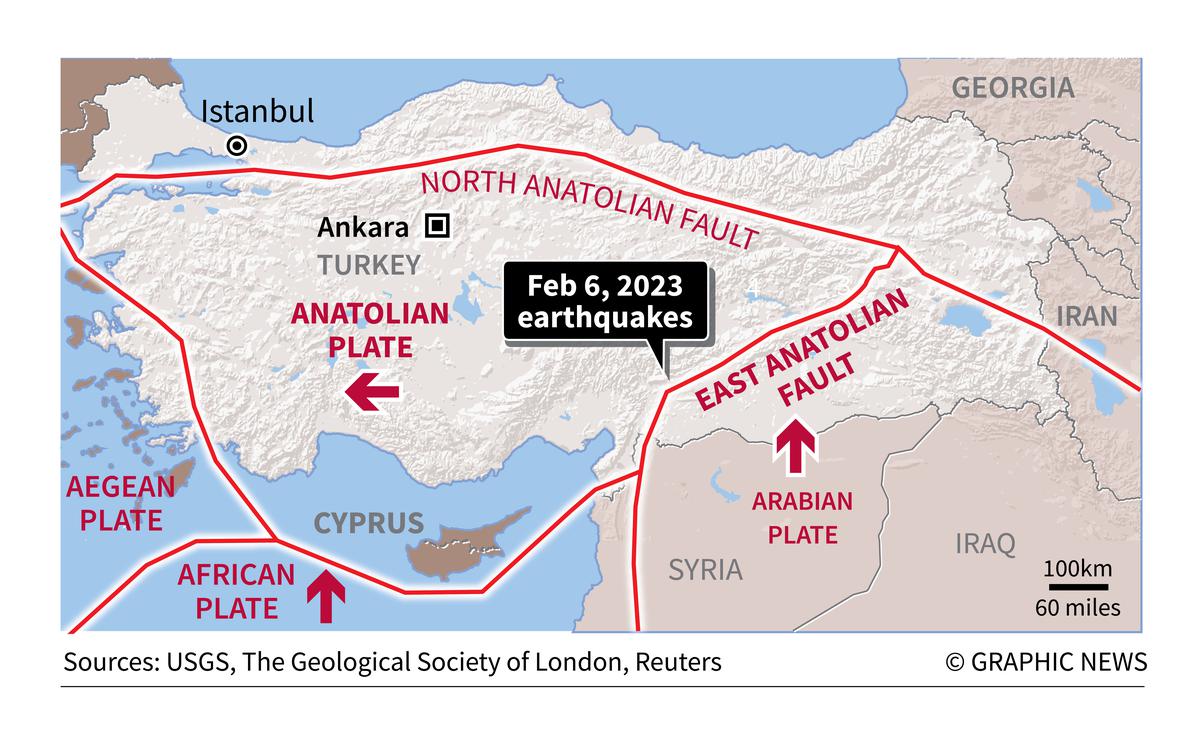
Geologists say that the earthquakes were from a ‘strike-slip’ which is typical of the earthquakes in the area.
Why were these earthquakes so devastating and lethal?
As this area hosts many fault techniques, there are numerous earthquakes being recorded in the area. Only those who end in a launch of vitality above a sure threshold are captured by seismological devices. At magnitude 7.8, the February 6 occasion is way greater than the ones the space has skilled earlier than. The fault system runs alongside practically 190 km which is why the influence of the earthquakes was so far-ranging.
The second earthquake, of seven.5 magnitude, occurred additional to the north on a distinct however adjoining fault system known as the Sürgü Fault. The magnitudes of those earthquakes counsel that there shall be a number of aftershocks that may be registered in a large radius and stories of shakes from as far-off as Cairo (950 km) and Istanbul (815 km) away have been reported.
Also Read | Three historic cities broken in Turkey-Syria quake
Are there similarities to earthquakes in India? Can vitality from latent strain be constructed up over the years?
The Indian Plate, colliding into the Eurasian plate and tilting upwards, created the Himalayas. The most typical kind of earthquake in the Himalayan area is because of reverse faults due to the compressive forces between the two plates, says Suvrat Kher, a Pune-based geologist. “However, whether it’s strike-slip or a thrust, the waves generated can be as powerful.” Scientists have longed warned of an enormous, overdue earthquake in the Garhwal-Kumaon vary right here due to what is understood about the sample of quakes in the area.
Based on the quantity of ‘slip’ (or motion) that’s noticed in an earthquake and measurements of the quantity of ‘strain’ that accumulates yearly, scientists can deduce the latent strain that’s build up alongside a fault has been launched. “We don’t have very accurate records that date back, say a thousand years, on 7+ magnitude earthquakes. The records of the last 300 or so years suggest that those that have occurred haven’t released all the pent-up energy and that’s why we think a major one — maybe even an 8 magnitude one — is overdue. However predicting the day it will occur is beyond our ken now,” stated V.Ok. Gahlaut, seismologist and professor at the National Geophysical Research Institute (NGRI), Hyderabad.
In the Turkey-Syria earthquakes, vitality from practically 300 years of amassed pressure was launched, he added.
How a lot does the magnitude of earthquakes correlate to the harm they inflict?
It is just broadly true that the magnitude of earthquakes corresponds to loss of life and devastation. Chile, a rustic with a protracted historical past of devastating earthquakes (over 9), is taken into account to be a mannequin for earthquake preparedness.
Despite experiencing earthquakes with magnitudes over 8 in 2014 and 2015 casualties are extraordinarily minimal attributable to years of strictly implementing constructing codes. This regardless of being a a lot poorer nation than Japan, additionally identified for its expertise in earthquake-proofing constructions.
The 9-magnitude earthquake that prompted a tsunami and a radiation leak in the nuclear energy plant in the nation’s Fukushima prefecture in 2011, didn’t harm the stability of the construction, stated Mr. Gahlaut. “Just as the energy released exponentially rises in a single step of the scale (Moment Magnitude), the cost of earthquake-proofing too rises exponentially. On the other hand, if structures are built on a fault line, then no amount of engineering can save them.”
An absence of enforcement of constructing codes in Turkey and the timing of the earthquake in the early morning are believed to be main components for the loss of life and devastation inflicted. “It’s a bit like India where we have lots of rules (on building codes) but there is limited enforcement. The 1993 Latur earthquake for instance was a little over 6 magnitude but caused enormous damage because building codes are not enforceable there,” stated Mr. Kher.
- Turkey and Syria lie at the confluence of three plates, making the area an especially seismically lively zone.
- As this area hosts many fault techniques, there are numerous earthquakes being recorded in the area.
- The magnitudes of those earthquakes counsel that there shall be a number of aftershocks that may be registered in a large radius


