In 2021, there have been greater than 14 billion mobile gadgets on the earth regardless that there have been solely 7 billion folks. The ubiquity of those gadgets – however particularly smartphones – has come to outline the modern period along with local weather change, antimicrobial resistance, and warfare. But for smartphones’ outsize mark on historical past, one important part of theirs has flown considerably below the radar: the SIM card.
What is a SIM card?
‘SIM’ stands for ‘subscriber identification module’. Specifically, it’s an built-in circuit, or a microchip, that identifies the subscriber on a given community.
Imagine every mobile community is a metropolis whose residents are recognized by a quantity, known as the worldwide cell subscriber id (IMSI), and their places by some knowledge. The SIM card is a subscriber’s ID card on this metropolis. When somebody needs to contact a subscriber on this metropolis, the community makes use of the subscriber’s SIM card to seek out them and make sure their id.
In order for a cell phone to hook up with any mobile community that follows the Global System for Mobile Communications (GSM) normal, a SIM card is obligatory. This relationship is established utilizing a novel authentication key – a bit of information {that a} person must ‘unlock’ entry to the community. Every SIM card shops this knowledge and it’s designed such that the person can’t entry it by means of their telephone. Instead, alerts despatched by the telephone into the community are ‘signed’ by the important thing, and the community makes use of the signature to grasp whether or not the telephone’s connection is reputable. It is feasible to duplicate a SIM card by accessing its key and storing it in a number of cards.
SIM cards additionally retailer details about its personal ID quantity (the built-in circuit card identifier), the IMSI, the subscriber’s location space id (i.e. their present location), a listing of most popular networks (to whom the subscriber can join when roaming), emergency numbers, and – relying on the area accessible – the subscriber’s contacts and SMS messages.
How does a SIM card work?
SIM cards are designed in accordance with the ISO/IEC 7816 worldwide normal maintained by – as its identify signifies – the International Organisation for Standardisation and the International Electrotechnical Commission. It applies to digital identification cards, together with sensible cards.
In this normal, the cardboard itself consists of the built-in circuit, which is glued to a silicon substrate on the highest aspect. On the opposite aspect of the substrate are steel contacts, which type the gold-coloured aspect of the SIM card. Wires join the built-in circuit from its backside aspect to the steel contacts on the highest aspect, and the contacts interface with the telephone’s knowledge connectors.
A cross-sectional view of the construction and packaging of a sensible card chip.
| Photo Credit:
Justin Ormont/Wikimedia Commons (CC BY-SA 3.0)
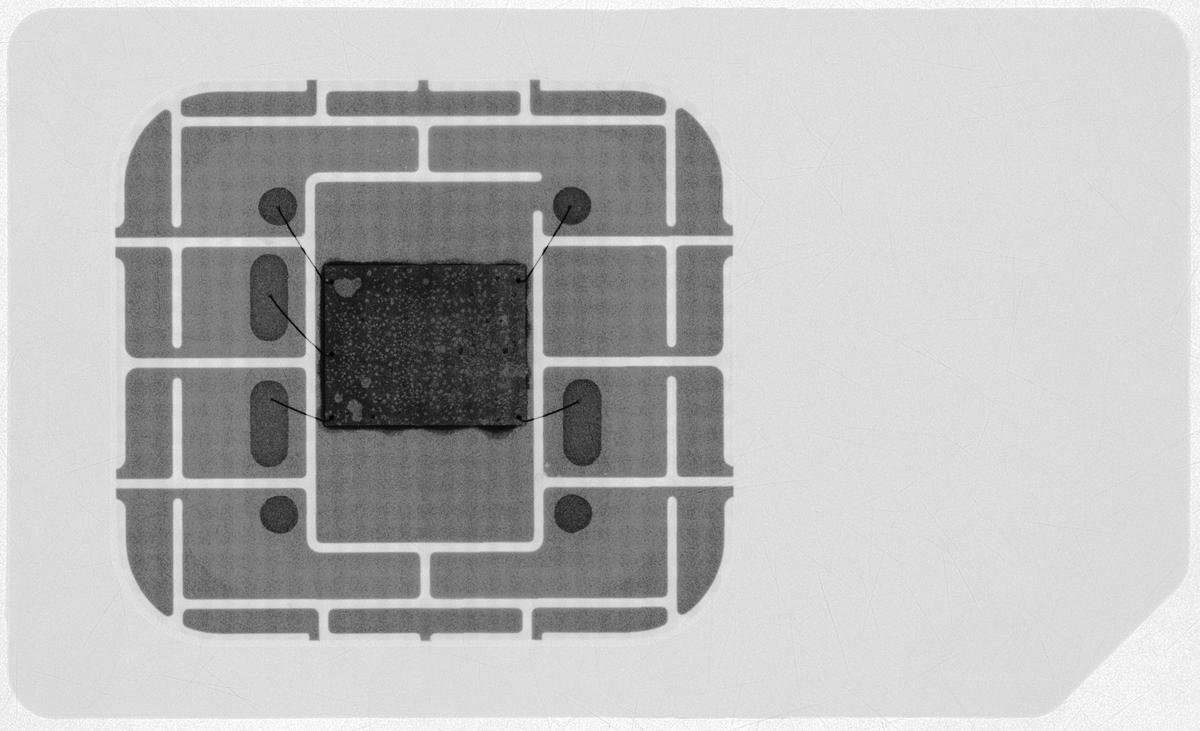
An X-ray of a mini-SIM exhibiting the microchip, the steel contacts, and the wires connecting them.
| Photo Credit:
SecretDisc/Wikimedia Commons, CC BY-SA 3.0
The steel contacts have a segmented look. Each phase is named a pin and has a selected function. For instance, pin 1 collects the working voltage that offers it the facility to function. Pin 3 is to entry the SIM’s clock and pin 5 is the grounding. Pin 7 transmits knowledge out and in of the SIM. These pin-wise roles are specified by the ISO/IEC 7816-2 normal; others, numbered 1 by means of 15, specify numerous features of a SIM card and the way they’re to be applied, from their “transmission protocols” to “cryptographic information applications”.
This is the {hardware} aspect (minus the telephone’s inside workings). On the community aspect, the SIM helps a telephone set up its place inside a mobile community. When a subscriber dials a recipient’s quantity, the telephone sends knowledge through the community – signed by the important thing on the SIM card – to a phone trade. If the recipient is related to the identical trade, the community establishes their id and the decision is routed to them. If the recipient is ‘located’ elsewhere, a pc related to the community routes the decision there in accordance with probably the most optimum route.
How have SIM cards modified?
SIM cards are a kind of sensible card, and the historical past of sensible cards begins within the late Nineteen Sixties, when West German engineer Helmut Gröttrup reportedly first had the thought to stay an built-in circuit in a plastic panel the dimensions of a bank card. The measurement and structure of this microchip developed in leaps and bounds within the subsequent many years, following Moore’s regulation.
The SIM card itself developed in accordance with the requirements that outlined the networks to which its customers wished to attach. The European Telecommunications Standards Institute (ETSI) ready the GSM Technical Specification 11.11 concerning the SIM card. The July 1996 version says it “defines the interface between the SIM and the Mobile Equipment (ME) for use during the network operation phase of GSM as well as those aspects of the internal organisation of the SIM which are related to the network operation phase, within the digital cellular telecommunications system.” This is all the pieces from its bodily options – together with working temperature and “contact pressure” – to authentication and knowledge entry traits.
GSM issues the second technology of mobile networks. After creating the 11.11 normal, ETSI transferred a few of its obligations to a global consortium of seven organisations known as 3GPP. (The Telecommunications Standards Development Society in India is one.) 3GPP subsequently developed the requirements for the third (3G), fourth (4G), and fifth technology (5G) of networks.
Until 2G networks, the time period ‘SIM card’ denoted each the {hardware} and the corresponding software program. This modified with the appearance of the Universal Mobile Telecommunications System with 3G networks, when ‘SIM’ grew to become solely the software program; the {hardware} was known as the Universal Integrated Circuit Card (UICC). The software program was additionally upgraded to an utility known as Universal SIM, or USIM, which may very well be modified to be suitable with the identification and safety necessities of 3G, 4G, and 5G networks. As a end result, a UICC loaded with each SIM and USIM functions can work with networks of all generations.
What is an eSIM?
Over the years, the SIM card has shrunk from the SIM to the mini SIM to the micro SIM to the nano SIM. The newest on this path is the eSIM, with specs outlined by the GSM Association. In the eSIM paradigm, the SIM software program is loaded to a UICC that’s completely put in within the cell gear within the manufacturing unit itself, i.e. it could’t be eliminated. (This is named the eUICC.)
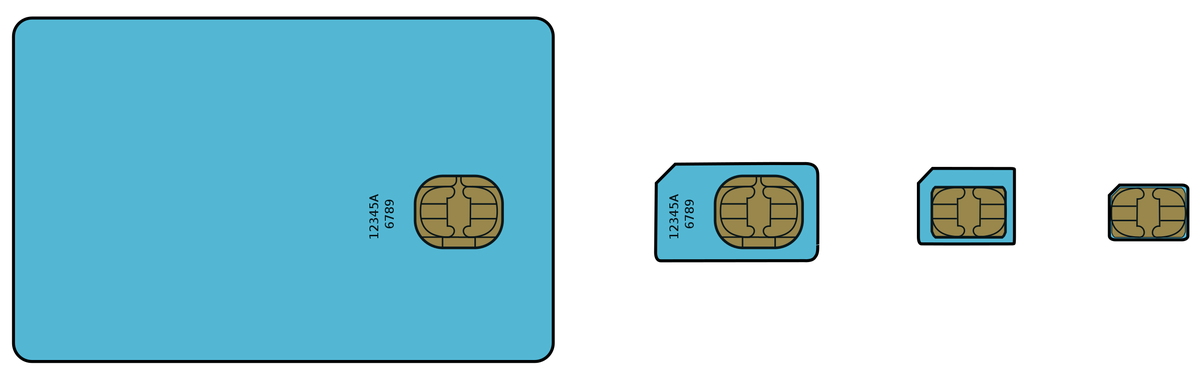
The measurement evolution of SIM cards by means of (L-R) full-size, mini, micro, and nano.
| Photo Credit:
Cvdr/Wikimedia Commons (CC BY-SA 3.0)
Users utilizing cell gear with this functionality – such because the Google Pixels 2, 3, and 4 or the iPhone 14 collection – don’t must trouble with bodily changing their SIM cards after they be part of or swap networks. Instead, the community operator merely has to reprogram the gear, which may also be carried out remotely.
An eSIM has two rapid benefits. First, it’s thought of to be environmentally friendlier than a bodily SIM: its reprogrammability means no want for extra plastic and steel for a brand new SIM. Second, if a malicious individual good points entry to your telephone, they received’t have the ability to individually entry the SIM utility nor have the ability to duplicate it.
There are additionally a minimum of two disadvantages. First, in some nations, together with the U.S., eSIMs could be programmed by subscribers themselves. But this course of may be tough for these with low digital literacy, such because the aged. Second, an eSIM can in idea permit community operators to trace subscribers’ knowledge, together with inside apps on the machine and particularly within the absence of information privateness legal guidelines.


