Model of the Mars 3 lander.
| Photo Credit: Space Museum flickr
When we discuss in regards to the area race between the Cold War adversaries the U.S. and the Soviet Union, we normally focus on the race to land the first human beings on the moon. Soon after this was achieved, nevertheless, consideration shifted to our neighbouring planet Mars. The first successful soft landing on Mars was achieved by the Soviet Union with their Mars 3 mission.
At this preliminary interval of planetary exploration, each these area superpowers tended to launch pairs of spacecraft as a precautionary measure. The thought was to have one because the backup of one other, in order that not less than one in all them succeeded in its efforts even when the opposite failed utterly in its goal.
It subsequently comes as no shock that the Mars 2 and Mars 3 missions consisted of an identical spacecraft. With a bus/orbiter module and an hooked up descent/lander module, the mixed mass of the spacecraft, with gasoline, was roughly 4,650 kg. The Mars 3 spacecraft was 4.1 metres excessive, 5.9 metres throughout the 2 photo voltaic panel wings and had a base diameter of two metres.
Primary aims
The main goal of the Mars 3 orbiter was to picture the martian floor and clouds, decide the temperature on Mars, and measure properties of the martian ambiance, amongst others. These have been along with serving as a communications relay to ship alerts from the lander to Earth.
Mars 3 was launched on May 28, 1971, simply 9 days after Mars 2 had been efficiently launched. Ten days later, on June 8, a mid-course correction was made after which Mars 3 was concerned in a three-way race with Mars 2 and U.S.’ Mariner 9 to change into the first spacecraft to orbit Mars.
Even although Mariner 9 was final off the blocks, having been launched on May 30, it turned the first to succeed in Mars on November 14. Mars 2 reached Mars on November 27 and Mars 3 made it to its vacation spot on December 2.
Achieves soft landing
Less than 5 hours earlier than reaching Mars, the descent module of Mars 3 had been launched. Having entered the martian ambiance at roughly 5.7 km/s, a mix of aerodynamic braking, parachutes, and retro-rockets allowed the lander to attain a soft landing. With the Mars 2 lander having crashed, this made the Mars 3 mission the first ever to attain a soft landing on Mars.
Only simply although, because the lander stopped transmitting and the devices stopped working lower than 20 seconds after the successful landing. While the explanations stay unknown, the large floor mud storms that have been raging on the time of landing might have brought about the lander to cease working.
As the orbiter had suffered a partial lack of gasoline, it couldn’t put itself into the deliberate 25 hour orbit. Instead, a truncated burn was carried out by the engine in an effort to put the spacecraft right into a 12 day, 19 hour lengthy orbit about Mars.
20 orbits round Mars
A big quantity of knowledge was despatched again by Mars 2 and Mars 3 orbiters from December 1971 to March 1972, although transmission continued until August. On August 22, 1972, an announcement was made stating that Mars 2 and Mars 3 had accomplished their missions. While Mars 2 had accomplished 362 orbits of the crimson planet, Mars 3 had carried out 20 orbits.
Apart from the 60 photos obtained from the probes, the info supplied by them revealed mountains as excessive as 22 km, atomic hydrogen and oxygen within the higher ambiance, and floor temperatures and pressures. The knowledge gathered not solely supplied info on the martian gravity and magnetic fields, but additionally helped create floor aid maps.
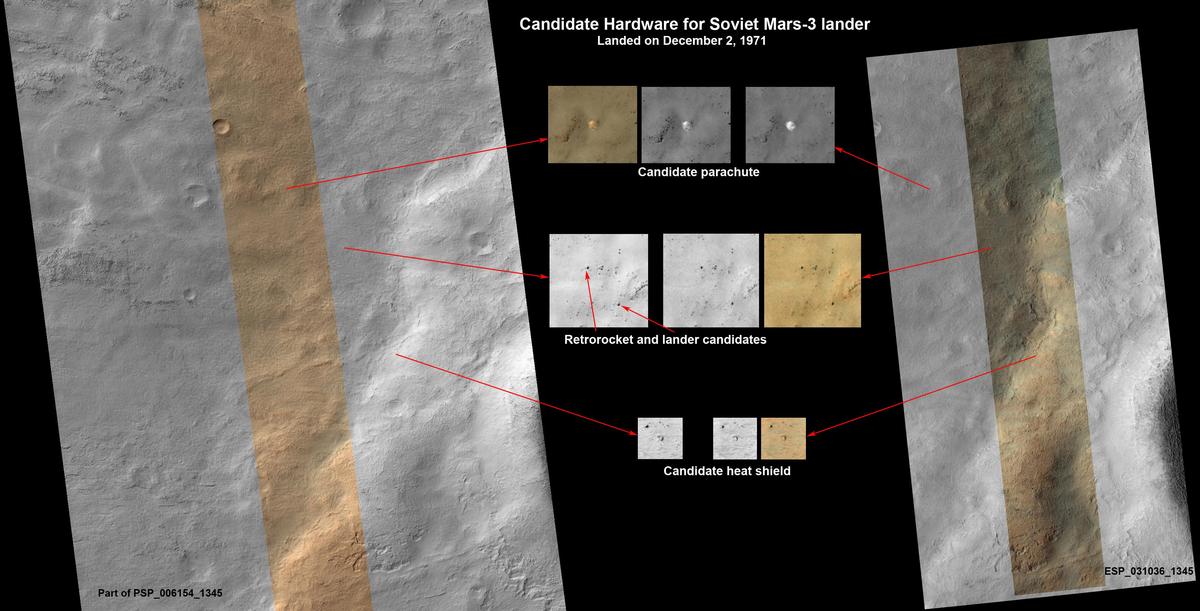
This set of photos reveals what may be {hardware} from the Mars 3 lander, seen in a pair of photos from the High Resolution Imaging Science Experiment (HiRISE) digicam on NASA’s Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter.
| Photo Credit:
NASA JPL Caltech Univ of Arizona Wikimedia Commons
Mars 3 was again within the information 4 many years later in April 2013 when citizen lovers discovered options of its {hardware} in a five-year-old picture from NASA’s Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter. The particles within the photos resembled what may need been the parachute, warmth protect, terminal retrorocket and lander. Regardless of whether or not these have been the particles of the Mars 3 lander or not, the mission did efficiently change into the first ever to attain a soft landing on our neighbouring crimson planet.


